Cashless transactions. Robust customer databases. The Internet of Things. In today’s hyper-connected world, it’s no surprise that cyber crime is at an all-time high with fraud being the primary motive.
Large, enterprise companies are often thought to be the primary target for cyber crimes, perhaps due to national headlines and volume of compromised records. However, according to several information security reports, it is small, private companies with less than 1,000 employees that make up nearly half of all cyber crime victims in the US.
In addition to facing the greatest number of attacks, small businesses typically incur the hardest impact due to their limited resources and inexperience to effectively address both proactively and reactively.
Despite all this, 43% of small businesses have no cybersecurity defense plan at all. In the rapidly-growing cannabis industry, cyber risk is a top concern for businesses of all sizes.
Why preventing fraud is important
Fraud can occur in many different forms, from business email compromise such as phishing or spoofing, social engineering, ransomware and check or wire transfer fraud. In many instances the funds are already gone and at best, difficult to recover by the time the crime is detected and reported to the associated financial institution and FBI.
Cannabis businesses like dispensaries, manufacturers, and cultivators are prime targets for these attacks because they’re relatively new, small operations with few dedicated IT resources. They collect sensitive customer information and have a reputation for being flush with cash.
Common types of cyber crime
The 2 most common types of cyber crime today are social engineering and ransomware, both of which can be significantly mitigated through risk management practices. Social engineering, or sometimes called fraudulent instruction, involves the psychological manipulation or deception of personnel to reveal sensitive information or perform a specific act such as transferring funds. Ransomware is a type of malicious software that once installed, holds computer systems and its data hostage in exchange for a ransom demand.
Below are best practices and recommended resource partnerships to help protect your organization.
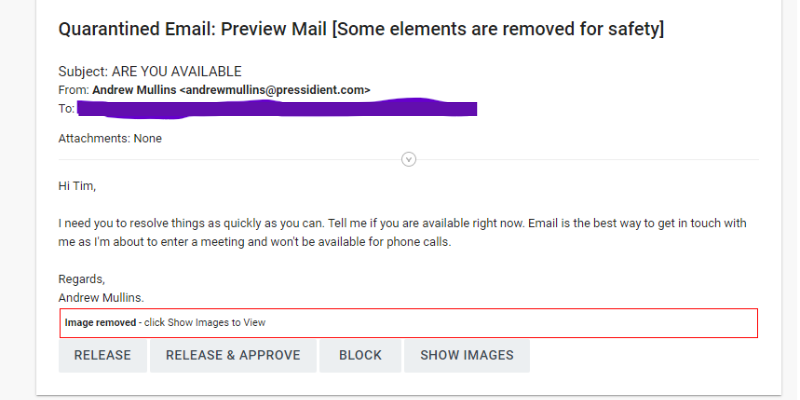
Social Engineering Email Example 2023
7 best practices to prevent cyberattacks
1. Educate and train employees
In both social engineering and ransomware attacks, the most common methods of intrusion are email and remote access hardware such as laptops and cell phones. Considering the human error element involved, the best first line of defense is educating and training your staff. We recommend to not only provide but require routine training around current trends in online scams, business email compromise and other common fraud schemes, deploy phishing simulations, all of which help with harboring a culture of information security.
2. Use multi-factor authentication
MFA is a multiple step log-in process that requires users provide two or more verification factors to gain access to applications such as email or management software. MFA should be enabled for all users including privileged accounts and especially those with remote access. While MFA has become an increasingly common and highly effective cybersecurity strategy, a sophisticated bad actor can target specific individuals and extract sensitive data over time, ultimately obtaining the credentials needed to gain access to their desired destination.
3. Verify any requests for invoice or payment changes
Business Email Compromise is one of the most financially damaging online crimes. Email spoofing is when a cybercriminal disguises themselves as a trusted source, often appears legitimate, and sometimes comes from a known vendor email address. They typically provide notification of a change to banking information and payment instruction. In addition to new payment instruction, another red flag is a rushed or urgent request to avoid detection. Since spoofing and social engineering have become increasingly refined criminal acts, one can never rely on email requests alone and should authenticate the request via a known contact phone number on file (and not the phone number within the unverified email!).
4. Protect your online environment
It is just as important to safeguard cyber environments as physical environments. Common and recommended cybersecurity practices include firewalled internet connections and Virtual Private Networks, encryption of sensitive data, keeping antivirus software updated with routine and automated scans, password complexity requirements with a quarterly changing cadence, and daily offsite or cloud backups of critical data. These are all practices that should be verified and if needed, rectified through an internal IT department or third-party managed services provider.
5. Report suspicious activity immediately
Suspected fraud or any type of internal cybercrime requires immediate action. The first parties notified should be the police or FBI, the associated financial institution and insurance provider. Halt all online activity and remove any applications that may have been compromised.
6. Partner with your financial institution
Be sure talk to your banker about services or products that can provide additional protection to your bank accounts. Positive Pay is a service that many financial institutions, like Triad Bank, offer to mitigate the potential loss with check fraud. If your company utilizes products such as online banking, bill pay, or Remote Deposit Capture, be sure features such as multi-factor authentication are enabled.
7. Purchase cyber liability insurance
Cyber losses, especially social engineering and ransomware, are typically not covered by general liability or D&O insurance policies. Proper coverage must be obtained through specialized cyber liability insurance products which can be difficult to find due to a narrow marketplace and limited distribution.
Cannabis businesses should look to industry specialized insurance agencies, such as POWERS Insurance & Risk Management’s cannabis division, for access to such policies. A robust cyber liability policy will include first- and third-party coverage and provide critical resources such as a breach response team. Obtaining cyber liability insurance requires qualification through completion of a thorough application, attesting to certain practices and standards such as MFA and routine data backups.
Co-Authors:
VP, BSA Officer Triad Bank
Commercial Practice Leader POWERS Insurance & Risk Management